CASE REPORT
A 62-year-old woman was referred after her optometrist noticed exudative retinopathy in her right eye. He also remarked that the patient had been complaining of reduced vision in the same eye.
The patient said that she felt her vision was deteriorating and that her optician had prescribed her reading spectacles. She had been diagnosed with hypertension recently and was taking appropriate treatment.
She had no notable previous ocular history, nor was there any family history of eye problems. She was well otherwise. Visual acuity was 6/36 in the patient’s right eye, with no improvement with the pinhole, and 6/9 in her left eye.
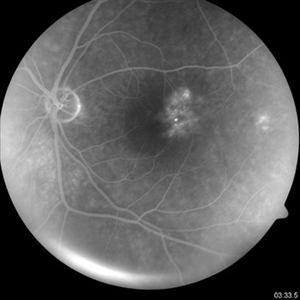
On examination, the anterior segment was relatively quiet with the iris, cornea, and lens unremarkable bilaterally. However, on examining the posterior pole of the right eye, a region of leaky vessels was noted juxtafoveally.
On closer inspection, a telangiectatic pattern of vessels was noted. Around these vessels was a circinate ring of hard exudates. The left eye was normal. A diagnosis of macular telangiectasia was made
Macular telangiectasia (Mac Tel) DISEASE entity
Macular telangiectasia (Mac Tel) leads to abnormalities of capillaries of the fovea or perifoveal region associated with loss of outer nuclear layers and ellipsoid zone that can progress to cystic cavitation-like changes in all retinal layers or development of full-thickness macular hole or subretinal neovascularization in advanced stages.
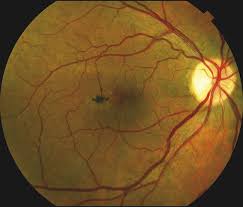
Macular telangiectasia (Mac Tel) is usually divided into 3 main groups:
- Type 1: congenital and unilateral. Thought to be similar to and/or possibly a variant of Coats disease. Uncommon.
- Type 2: acquired and bilateral. The most common form of the three types. Usually found in middle-aged or older patients.
- Type 3: a poorly understood primarily occlusive phenomenon that is quite rare.
Macular telangiectasia (Mac Tel) MANAGEMENT
There have been no randomized clinical studies for this entity. In non-neovascular cases, laser, intravitreal anti-VEGF, or steroid has not been shown to be effective in controlling the disease.
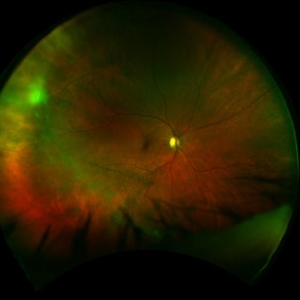
For neovascular cases, intravitreal anti-VEGF is the mainstay of treatment, although transpupillary therapy and photodynamic therapy have been used in the past. Neuroprotective agents are currently being investigated.
A Phase II trial studying intraocular delivery of ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) in eyes with Macular telangiectasia (Mac Tel) type 2 found decreased ellipsoid zone loss, increased macular thickness, and stable reading speed when compared to controls.
Phase III multi-center Renexus (NT-501) Trial is currently underway in testing the safety and efficacy of ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) in patients with macular telangiectasia type 2 in Phase 3 clinical trial.
This is a multi-center trial. Associated full-thickness macular holes may be treated with pars plana vitrectomy surgery, membrane peeling, and gas tamponade, but are likely to have a lower-than-average closure rate.
Prognosis
According to the Macular telangiectasia (Mac Tel) Project, 50% of type 2 patients with have a visual acuity of 20/32 or better, with a mean visual acuity of 20/40. Mac Tel can rarely lead to 20/200 or worse vision when associated with a full-thickness macular hole or subretinal neovascularization that can lead to a disciform scar in very advanced stages.
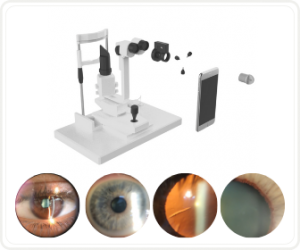
Would you have interest in taking retina images by smartphone?
Fundus photography is superior to fundus analysis as it enables intraocular pathologies to be photo-captured and encrypted information to be shared with colleagues and patients.
Recent technologies allow smartphone-based attachments and integrated lens adaptors to transform the smartphone into a portable fundus camera and Retinal imaging by smartphone.
RETINAL IMAGING BY YOUR SMARTPHONE
REFERENCES
1. Clemons TE, Gillies MC, Chew EY, Bird AC, Peto T, Wang JJ, Mitchell P, Ramdas WD, Vingerling JR; Macular Telangiectasia Project Research Group. Medical characteristics of patients with macular telangiectasia type 2 (MacTel Type 2) MacTel project report no. 3. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2013 Apr;20(2):109-13.
2. Wu L, Evans T, Arevalo JF. Idiopathic macular telangiectasia type 2 (idiopathic juxta foveolar retinal telangiectasis type 2A, Mac Tel 2). Surv Ophthalmol. 2013 Nov-Dec;58(6):536-59.
3. Charbel Issa P, Gillies MC, Chew EY, Bird AC, Heeren TF, Peto T, Holz FG, Scholl HP. Macular telangiectasia type 2. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2013 May;34:49-77.
RETINAL IMAGING BY YOUR SMARTPHONE
RETINAL IMAGING BY YOUR SMARTPHONE