CASE REPORT
A 75-year-old patient presented with decreased central vision in the right eye after cataract surgery which was done recently. He presented with no significant ocular or systemic history. His VA report was as follows RE: 6/18, LE: 6/9.
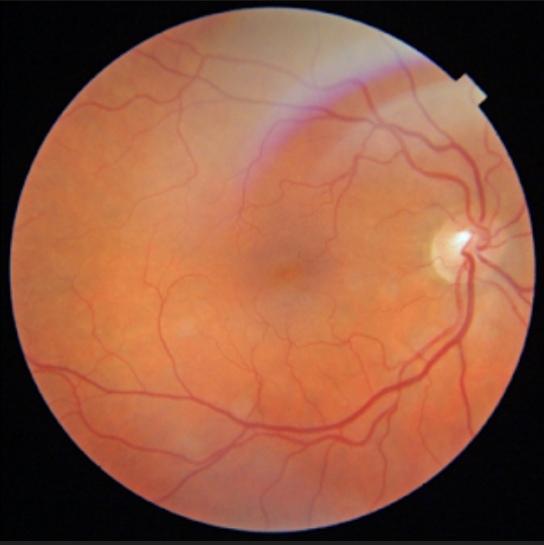
Pupillary reflexes, adnexa, anterior segment, ocular motility, and Intraocular pressure all were normal. On dilated fundus examination, the macular area appeared elevated or edematous due to the accumulation of fluid in the macular area.
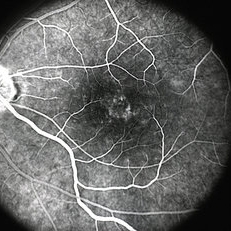
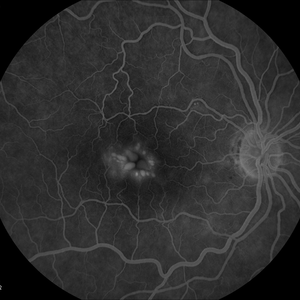
Fluorescein Angiography(FA) indicated leakage of fluorescein dye in retinal tissues. Optical Coherence tomography (OCT) showed retinal elevation with cystic spaces present in between the retinal layers.
Cystoid macular edema entity
As the name suggests, Fluid filled cyst-like spaces occur at the central retina called the macula and cause its swelling in the form of edema.
Disruption of the normal blood-retinal barrier causes thickening of the central retina which in turn leads to leakage of retinal capillaries and fluid gets accumulated in the intracellular spaces of the retina. This is a mostly painless and asymptomatic disorder.
The exact etiology is unknown, but some diseases cause CME like:
- Intraocular inflammation such as uveitis can further leads to Macular inflammation.
- Age-related Macular degeneration: In wet ARMD, abnormal blood vessels become permeable and leak fluid into the retina involving the macula thus leading to CME.
- Diabetic retinopathy: (Edema caused by it is diabetic macular edema).
- Central or branch retinal vein occlusion.
Due to occlusion of retinal veins, blood flow is disrupted thus contributing to CME
- Retinitis pigmentosa: This hereditary disease is also considered an etiological factor of CME
- Some surgical procedures can also lead to CME such as:
- Patients who have undergone cataract surgery are at increased risk of CME.
- Pars plana Vitrectomy (PPV)
- Photocoagulation
- Cryopexy
- Glaucoma surgery
The patient may present with the following complaints:
- Decreased vision
- Metamorphopsia (a condition in which an object appears wavy when looking straight ahead at the object).
- Micropsia
- Loss of color vision
- Loss of contrast sensitivity
- Central scotoma
Cystoid macular edema management
Medical treatment:
- Corticosteroids :
They can be given as a topical, periocular, or systemic intravitreal injection or implant.
E.g Intravitreal triamcinolone can be helpful in reducing fluid accumulation and decreasing VEGF production.
Four categories of intravitreal implants are as follows
- Dexamethasone biodegradable implant
- Helical triamcinolone acetonide implant
- Fluocinolone acetonide implant
- Injectable Fluocinolone acetonide
Their side effects may include cataract formation and glaucoma
- Anti VEGF :
These include ranibizumab and bevacizumab
- Carbonic Anhydrase inhibitors (CAIs)
- Pharmacologic vitreolysis agents
Surgical Treatment:
- PPV (Pars Plana Vitrectomy)
Would you have interest in taking retina images by smartphone?
Fundus photography is superior to fundus analysis as it enables intraocular pathologies to be photo-captured and encrypted information to be shared with colleagues and patients.
Recent technologies allow smartphone-based attachments and integrated lens adaptors to transform the smartphone into a portable fundus camera and Retinal imaging by smartphone.
RETINAL IMAGING BY YOUR SMARTPHONE
REFERENCES
- Abe T, Hayasaka S, Nagaki Y, et al. Pseudophakic cystoid macular edema treated with high-dose intravenous methylprednisolone. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1999;25:1286–8.
- Aiello LP, Pierce EA, Foley ED, et al. Suppression of retinal neovascularization in vivo by inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) using soluble VEGF-receptor chimeric proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92:10457–61.
- Aiello LP, Bursell SE, Devris T, et al. Protein kinase C beta selective inhibitor LY333531 ameliorates abnormal retinal hemodynamics in patients with diabetes. Diabetes. 1999;48:A19.
- Gass JD, Norton EW. Follow-up study of cystoid macular edema following cataract extraction.Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1969;73:665-682.
- Hogan P, Dall T, Nikolov P. American Diabetes Association: Economic costs of diabetes in the US in 2002. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:917-932.
- DeCross FC, Afshari NA: Perioperative antibiotics and anti-inflammatory agents in cataract surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 2008;19:22–26.
- Panchapakesan J, Rochtchina E, Mitchell P: Five-year change in visual acuity following cataract surgery in an older community: the Blue Mountains Eye Study. Eye 2004;18:278–282.
RETINAL IMAGING BY YOUR SMARTPHONE
RETINAL IMAGING BY YOUR SMARTPHONE