Abstract
Meibomian Gland Adenoma (MGA) is a prevalent benign tumor affecting the meibomian glands of animals, particularly dogs.
Early detection and proper management are pivotal for safeguarding the ocular health and overall well-being of afflicted animals.
Meibomian Gland Adenoma Disease Entity
Meibomian Gland Adenoma (MGA), alternatively termed meibomian gland adenocarcinoma or sebaceous gland adenoma, manifests as a benign tumor originating from the meibomian glands, which are sebaceous glands located within the eyelids.
Predominantly occurring in older animals, MGA primarily affects dogs, although it can also affect other species. While the precise etiology of MGA remains elusive, genetic predisposition and hormonal influences are theorized to contribute to its pathogenesis.
Clinical Presentation
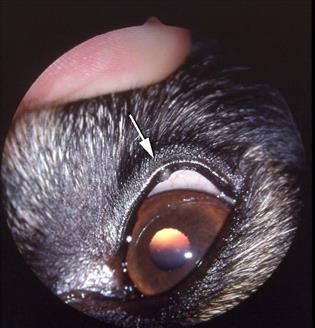
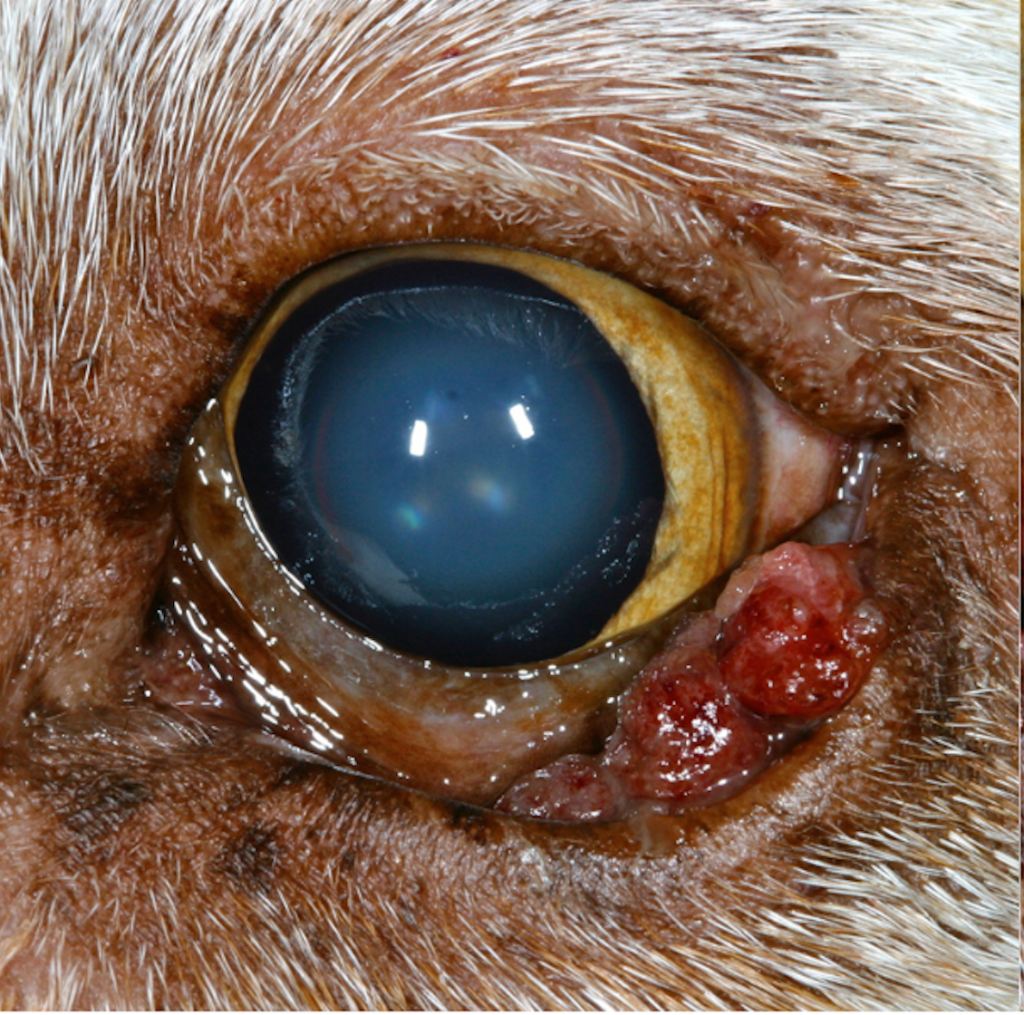
MGA typically presents as a gradual, painless mass within the eyelid margin or on the conjunctival surface. These tumors often exhibit well-defined borders and firm consistency.
In certain instances, MGA may induce ocular discomfort, excessive tearing (epiphora), or secondary corneal ulceration due to mechanical irritation from the mass abrading against the cornea.
Meibomian Gland Adenoma Diagnosis
The diagnosis of MGA typically entails a comprehensive ophthalmic examination conducted by a qualified veterinarian or veterinary ophthalmologist. This examination encompasses:
- Physical Examination: Thorough palpation of the eyelids to identify any palpable masses or abnormalities.
- Slit-lamp Biomicroscopy: Detailed evaluation of the eyelids, conjunctiva, and cornea utilizing a slit-lamp biomicroscope to assess the size, location, and characteristics of the tumor.
- Histopathology: Surgical biopsy or excision of the tumor followed by histopathological analysis to confirm the diagnosis and evaluate for any malignant potential.
Meibomian Gland Adenoma Treatment
Primary treatment modalities for Meibomian Gland Adenoma in animals involve surgical excision of the tumor. Depending on the tumor’s size, location, and the animal’s overall health status, surgical options may include:
- Eyelid Mass Excision: Complete excision of the tumor with a margin of healthy tissue to minimize the risk of recurrence.
- Cryotherapy: Cryosurgery may be employed as an adjunctive treatment to eradicate any residual tumor cells post-surgical excision.
- Topical Medications: In scenarios where complete surgical excision is unattainable, topical medications like corticosteroids or immunomodulators may be prescribed to mitigate inflammation and diminish tumor size.
Regular follow-up examinations are imperative to monitor for tumor recurrence or progression.
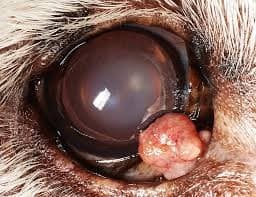
Prognosis
The prognosis for animals diagnosed with Meibomian Gland Adenoma is generally favorable following surgical excision.
However, tumor recurrence may ensue in select cases, necessitating further therapeutic interventions. Timely detection and intervention serve as pivotal determinants in achieving a favorable clinical outcome.
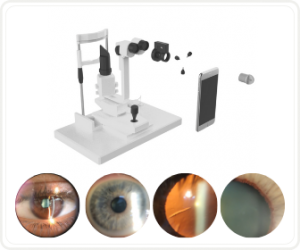
HOW TO TAKE SLIT-LAMP EXAM IMAGES WITH A SMARTPHONE?
Smartphone slit-lamp photography is the new advancement in the field of science and technology in which photographs of the desired slit-lamp finding can be taken with smartphones by using the slit-lamp adapters.
Slit-lamp Smartphone photography
References
- Labelle, A. L., Labelle, P., & Hamor, R. E. (2018). Ophthalmic neoplasia in the dog and cat. Veterinary Clinics of North America: Small Animal Practice, 48(5), 883-900.
- Maggs, D. J. (2018). Eyelid tumors. In Veterinary Ophthalmology (6th ed., pp. 1101-1114). John Wiley & Sons.
- Wilcock, B. P., & Peiffer, R. L. (2019). Histologic classification of eyelid tumors of domestic animals. Veterinary Pathology, 56(2), 195-204.
- Leis, M. L. (2004). Canine ocular neoplasia: a review of eyelid tumors. Veterinary Ophthalmology, 7(5), 269-282.
Slit-lamp Smartphone photography
RETINAL IMAGING BY YOUR SMARTPHONE