CASE REPORT
A 9-year-old girl presented with a chief complaint of poor vision and difficulties in reading and recognizing faces.
Concerns about her vision had been noted by her parents when she was just 3 years old, with observations of squinting and holding objects close to her eyes.
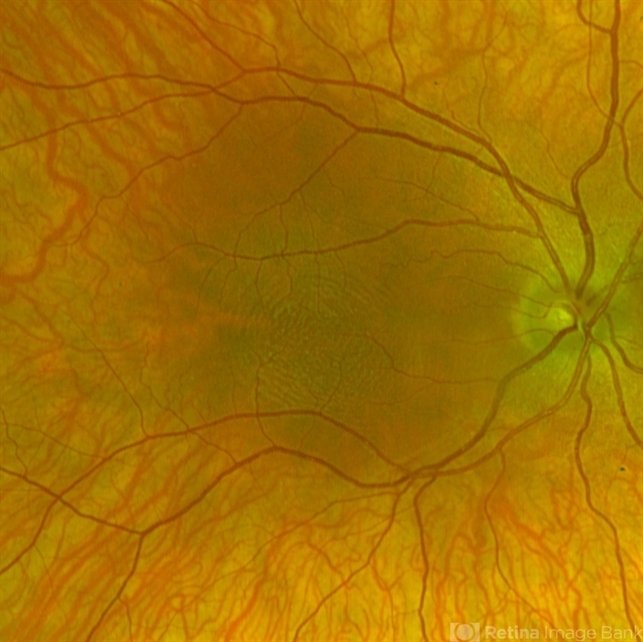

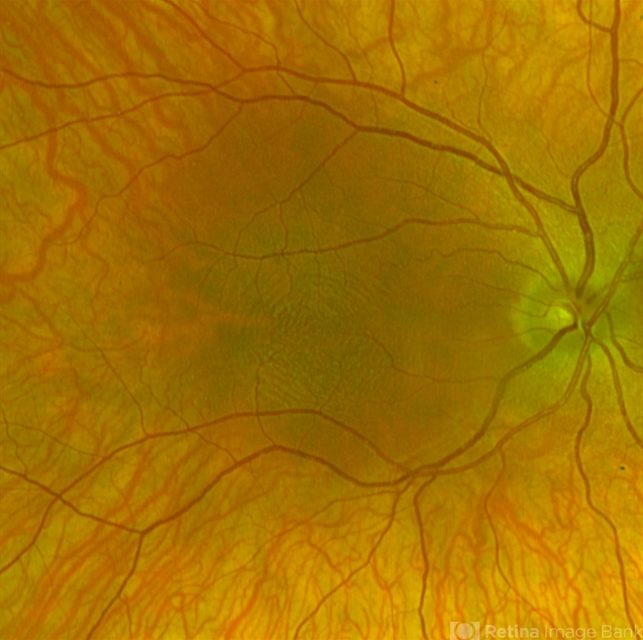
Ophthalmic examination revealed significantly reduced visual acuity in both eyes, with the best-corrected vision measuring at 20/200. Continuous horizontal nystagmus was observed during fixation and pursuit movements, and fundus examination showed pale and atrophic foveal regions in both eyes.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) scans confirmed the absence of a well-defined foveal pit, consistent with foveal hypoplasia.
Genetic testing was subsequently performed due to the clinical presentation and the absence of ocular disorders in the family, ultimately revealing a mutation in the HMX1 gene, confirming the diagnosis of foveal hypoplasia.
Foveal Hypoplasia DISEASE entity
Foveal hypoplasia is an ocular abnormality in which the foveal pit either fails to develop, or does not completely develop, and is associated with poor visual acuity and nystagmus.
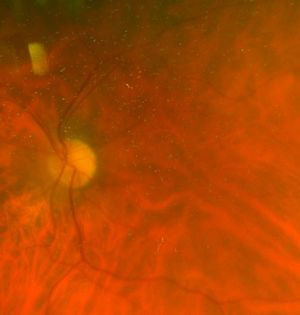

It may present in isolation or be associated with other conditions such as albinism, coloboma, optic nerve hypoplasia, retinopathy of prematurity, and aniridia.
Risk factors that affect foveal development, such as prematurity, can lead to foveal hypoplasia.
Although the foveal pit does not fully develop in foveal hypoplasia, there is developmental plasticity in the retina that allows cone cells in the foveal area to change their own shape to allow for a higher cone cell density in the fovea.
This, in the most basic sense, allows for the central area of the eye and brain to increase the sampling rate of each photon that enters the retina.
Early descriptions of foveal hypoplasia in the early 1900s were in association with other diseases, particularly hereditary nystagmus while assessing for retinal abnormalities with an ophthalmoscope.
Other conditions were later discovered to be associated with foveal hypoplasia, including macular aplasia, macular coloboma, and albinism.
Later use of imaging techniques such as fundus fluorescein angiography to identify absent foveal avascular zones (FAZ) has found cases of isolated foveal hypoplasia without associated nystagmus or comorbidities.
A cross-sectional study by Noval et al with 286 healthy children found that up to 3% of children had an anatomically underdeveloped foveal pit (fovea plana) bilaterally on OCT (optical coherence tomography).
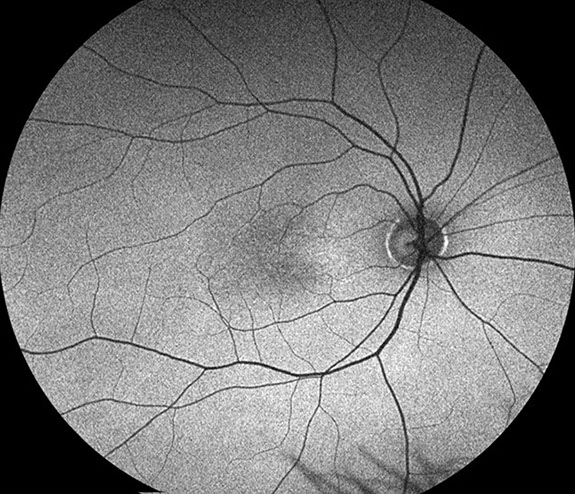

Because foveal hypoplasia is commonly associated with a number of ocular diseases, there does not seem to be a widely accepted standalone statistic on its prevalence or incidence in isolation.
However, many studies show the frequency of foveal hypoplasia occurrence in associated diseases.
Diagnosis of Foveal Hypoplasia
Signs and Symptoms:
Foveal hypoplasia is commonly seen with other conditions such as albinism, nystagmus, achromatopsia, iris abnormalities like aniridia, cataracts, and other ocular abnormalities.
Histologic analysis and OCT studies have revealed that the structure of the macula resembles peripheral retinal tissue with the persistence of ganglion and nuclear layers.
Ophthalmoscopy shows the absence of the foveal pit and FAZ. Most patients with foveal hypoplasia have poorer than normal visual acuity ranging between 20/50 to 20/200.
Absent foveal depression and persistence of inner retinal layers through the expected area of fovea as demonstrated by Heidelberg Spectralis OCT.
Diagnostic Procedures/ Testing:
Historically, the diagnosis of foveal hypoplasia was made in nystagmus evaluation with the ophthalmoscopic examination of the fundus.
Findings commonly included the absence of foveal pigmentation and the foveal reflex Introduction of fluorescein angiography allowed for visualization of the FAZ, and a small or absent FAZ coupled with ophthalmoscopy support the diagnosis of foveal hypoplasia.
Non-invasive imaging such as OCT and OCT-A (optical coherence tomography angiography) are now commonly used to evaluate the morphology and vasculature of the retina, respectively.
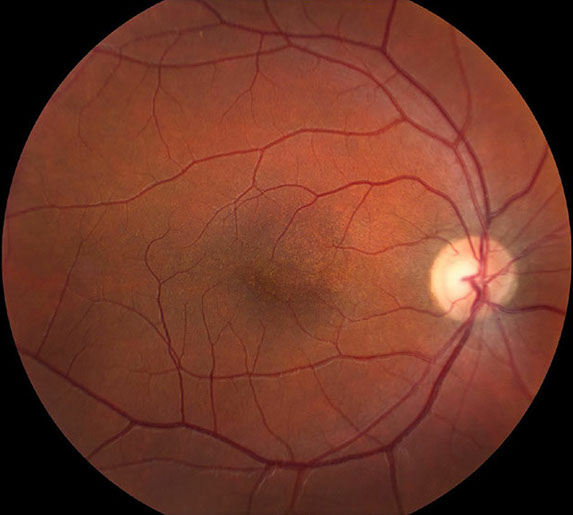

In foveal hypoplasia, OCT evaluation reveals the absence of the foveal pit and the persistence of inner retinal layers through the area where the foveal center is expected.
OCT-A evaluation of the FAZ shows an absence at the superficial capillary plexus and a variable decrease in the deep capillary plexus.
Foveal Hypoplasia MANAGEMENT
The management includes management of the associated ocular and systemic disorders, refractive correction, management of amblyopia, and low vision aids.
Patients with significant cataracts may benefit from cataract surgery though visual outcome is limited by the severity of foveal hyoplasia. Genetic counseling and analysis for genetic mutations form an important part of management in cases.
Would you have interest in taking retinal images with your smartphone?
Fundus photography is superior to fundus analysis as it enables intraocular pathologies to be photo-captured and encrypted information to be shared with colleagues and patients.
Recent technologies allow smartphone-based attachments and integrated lens adaptors to transform the smartphone into a portable fundus camera and Retinal imaging by smartphone.
RETINAL IMAGING BY YOUR SMARTPHONE
REFERENCES
- Duke-Elder, S. System of Ophthalmology 1963 3 St Louis CV Mosby.
- Kondo, H. Foveal hypoplasia and optical coherence tomographic imaging. Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2018 Oct-Dec;8(4):181-188. doi: 10.4103/tjo.tjo_101_18. PMID: 30637189; PMCID: PMC6302563.
- Bringmann, A., Syrbe, S., Görner, K., Kacza, J., Francke, M., Wiedemann, P., Reichenbach, A. The primate fovea: Structure, function and development, Progress in Retinal and Eye Research, Volume 66, 2018, Pages 49-84, ISSN 1350-9462, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2018.03.006.
- Provis, J.M., Dubis, A.M., Maddess, T., Carroll, J. Adaptation of the central retina for high acuity vision: cones, the fovea, and the avascular zone. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2013 Jul;35:63-81. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2013.01.005. Epub 2013 Mar 15. PMID: 23500068; PMCID: PMC3658155.
- Koyanagi, Y. Über den genetischen Zusammenhang zwischen dem hereditären Nystagmus und Bulbus Albinismus. Klin Monatsbl Augenheilkd 1927; 79: 43- 8.
- Holm, E. Hereditary nystagmus. Acta Ophthalmol (Kbh) 1926; 4: 20-7.
- Uemura Y, Kumanomido A. [The study on macular findings in “amblyopic eye”. Report I. Macular coloboma, macular aplasia, and macular hypoplasia]. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 1961 Nov 10;65:2264-71. Japanese. PMID: 13923531.
RETINAL IMAGING BY YOUR SMARTPHONE

RETINAL IMAGING BY YOUR SMARTPHONE